Execution Context
‘실행 문맥’이라고도 한다.
A box, a container, or a wrapper, which stores variables and in which a piece of out code is evaluated and executed.
즉, variables와 평가되고 실행할 코드들의 뭉치들을 말한다.
Default는 언제나 Global Execution Context이다.
Execution Context Object
Execution Context는 Object와 연관되어 있고 구성은 다음 그림과 같다.

생성단계는 크게 두가지로 나뉘고 순서대로 진행된다.
- Creation Phase
- Variable Object(VO) 생성
- Scope Chain 생성
- ‘this’ variable 값 설정
- Execution Phase
- 생선된 현재 Execution Context의 코드를 한줄 씩 읽어나간다.
Execution context stack
Exectuion context는 정의가 아닌 function을 불럿을 때 stack에 쌓이게 된다.
var name = 'John';
function first(){
var a = 'Hello!';
//두번째
second();
var x = a + name;
//function에 모든게 진행되면 function은 return하고 stack에서 pop up 된다.
}
function second(){
var b = 'Hi!';
//세번째
third();
var z = b + name;
}
function third(){
var c = 'Hey!';
var z = c + name;
}
//첫번째 Execution context가 stack에 쌓임
first();
![ExecutionStack]](/assets/img/aboutJavaScript/ExecutionStack.png)
Variable Object(VO)
3가지 과정이 있고 마지막 두 과정을 ‘Hoisting’이라고 한다.
- argument Object가 만들어지고 이는 function에 관련된 모든 argument를 포함한다.
- function declaration을 확인하고, 각 function은 function을 가리키는 property를 VO안에 만들게 된다.
- variable declration을 확인하고, 각 variable은 VO에 만들어지고 ‘undefined’로 세팅된다.
주의 할 점은 function은 실행 페이즈 전에 이미 정의되어 있지만
변수는 undefined로 정의가 되어있다는 차이점이 있다.
// functions
//function declaration은 hoisting을 통해 실행 페이즈 전에 정의가 된다.
calculateAge(1965);
function calculateAge(year) {
console.log(2016 - year);
}
//이건 function declaration이 아니라 function expression이기 때문에 에러이다.
// retirement(1956);
var retirement = function(year) {
console.log(65 - (2016 - year));
}
// variables
//var age가 정의되기 전이므로 hoisting으로 변수 선언문을 통해 undefined로 세팅이 먼저 된다.
console.log(age); //undefined
var age = 23;
function foo() {
//foo안의 age는 foo의 execution context의 VO안에 포함 된 것들을 사용한다.
console.log(age); //undefined
var age = 65;
console.log(age); //65
}
foo();
//여기 age는 global execution context의 VO안에 포함 된 것들을 사용한다.
console.log(age); //23
Scope Chain
scoping answers the question “where can we access a certain variable?”
각 function은 scope를 만든다. ES6에선 {}도 하나의 scope이다.
Lexical scoping : a function that is lexically within another function gets access to the scope of the outer function(aka. parent function)
하지만 자식 function으로 거꾸로 접근할 수는 없다.
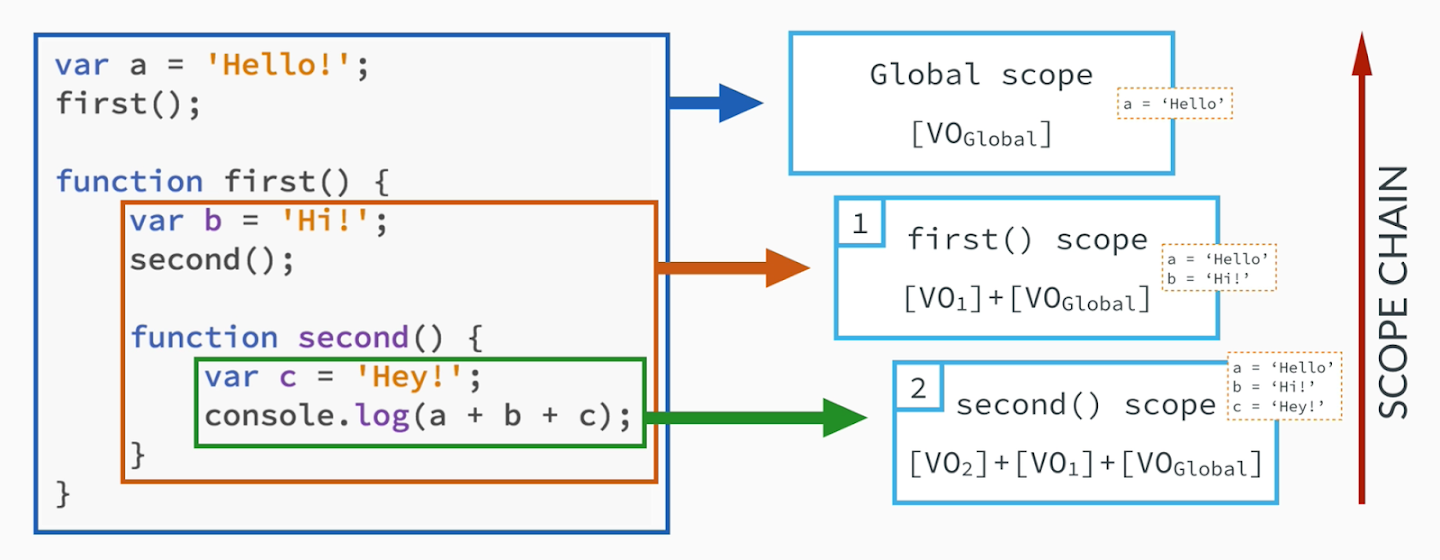
Exectuion Stack vs Scope Chain
execution stack은 function이 call된 순서대로 쌓이지만
scope chain은 function이 쓰인 순서대로 적용이 된다.

var a = 'Hello!';
first();
function first() {
var b = 'Hi!';
second();
function second() {
var c = 'Hey!';
//third function을 부를 수 있는 이유
//third는 hoisting되어 global execution context에 있기 때문에
//lexical하게 second가 접근할 수 있기 때문
third();
}
}
function third() {
var d = 'John';
//그러나 var c가 오류인 이유는 부모 function은 접근할 수 있지만 자식 function은 접근 할 수 없기 때문이다.
//console.log(c);
//a는 lexical하게 global execution context에서 가져 올 수 있고 d는 자신이 가지고 있다.
console.log(a+d);
}
this
The ‘this’ keyword is not assigned a value until a function where it is defined is actually called.
//regular function은 global object에 붙어있어 그 안의 this는 global object를 가리킨다.
//function calculateAge은 global object에 붙어있기 때문에 function calculateAge안의 this -> global object이다.
calculateAge(1985);
function calculateAge(year) {
console.log(2016 - year);
console.log(this);
}
var john = {
name: 'John',
yearOfBirth: 1990,
calculateAge: function() {
//john object가 이 method를 불럿으므로
//this -> john object
console.log(this); //john
console.log(2016 - this.yearOfBirth); //26
/*
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
john object의 method는 calculateAge이다.
calculateAge method안에 있는 innerFunction은 john object의 method가 아니므로
regular function이 되며 regular function의 this는 항상 window object를 가리킨다.
*/
function innerFunction() {
console.log(this); //window
}
innerFunction();
}
}
john.calculateAge();
var mike = {
name: 'Mike',
yearOfBirth: 1984
};
mike.calculateAge = john.calculateAge;
//method를 부르는 object가 달라졌기 때문에 this는 달라진 object를 바라보게 된다.
mike.calculateAge(); //john, 26