Heap?
최댓값 및 최솟값을 찾아내는 연산을 빠르게 하기 위해 고안된 완전이진트리(complete binary tree)를 기본으로 한 자료구조(tree-based structure)
보통 Priority Queue를 만들때 사용하고 Graph Traversal에서도 주로 사용된다.
2가지의 형태가 있다.
MaxBinaryHeap
부모 node가 child node보다 항상 크다.
MinBinaryHeap
부모 node가 child node보다 항상 작다.
용도
Priority Queue를 만들때 사용한다.
Tree 구조 형성의 법칙
- 최대한 짧게 만든다. = 좌우를 다 채운다음에 자식을 내린다.
- 왼쪽을 먼저 채운다.
- 친척사이는 서로 전혀 영향을 주지 않는다. = 같은 자식사이라면 서로의 숫자가 뭐가 오든 부모와의 대소 관계가 성립하면 상관 없다.
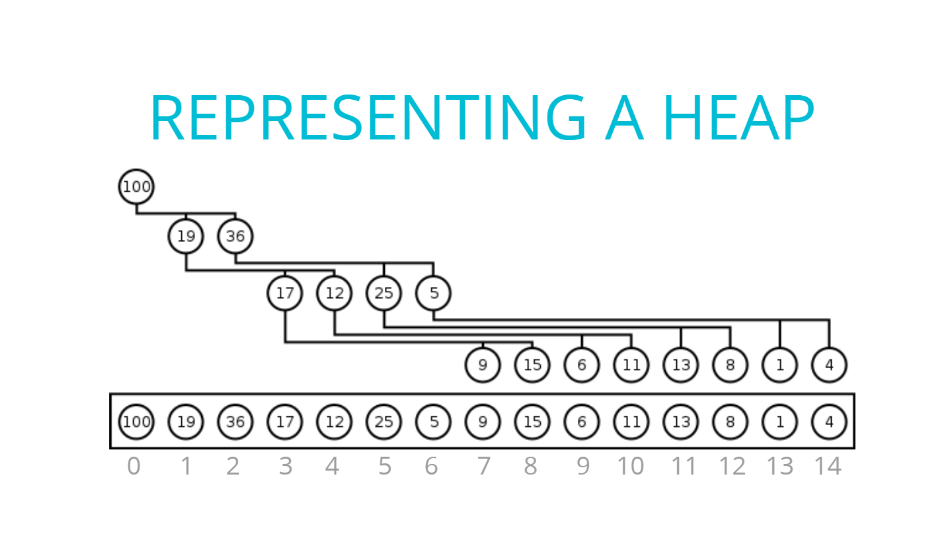
Representate as Array
Heap을 Array로 펼쳐 넣었을 때, 부모와 자식과의 index 관계는 부모의 index를 n이라고 할 때,
Left child Index = 2n + 1
Right child Index = 2n + 2
의 관계를 가진다.
반대로는 (n-1)/2 혹은 (n-2)/2의 관계를 가진다.
Insert
직접 구현
/*
Heap : 최댓값 및 최솟값을 찾아내는 연산을 빠르게 하기 위해 고안된 완전이진트리(complete binary tree)를 기본으로 한 자료구조(tree-based structure)
구현
- Heap은 bubble up 이라는 동작으로 정렬한다.( = 부모랑 자식이랑 비교해서 위치를 정렬)
- Array로 구현시 (부모index * 2 + 1) = left , (+ 2) = right이다.
*/
public class Heap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(41);
list.add(39);
list.add(33);
list.add(18);
list.add(27);
list.add(12);
Heap heap = new Heap();
list = heap.insert(list, 55);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
System.out.println(list.get(i));
//result : [55, 39, 41, 18, 27, 12, 33]
}
}
public ArrayList<Integer> insert(ArrayList<Integer> list, int element){
//가장 끝에 새로 추가 할 것을 넣고
list.add(element);
//정렬한다.
list = bubbleUp(list);
return list;
}
public ArrayList<Integer> bubbleUp(ArrayList<Integer> list){
int index = list.size() - 1;
//가장 끝에 추가된 새로운 element를 꺼낸다.
int element = list.get(index);
while(index > 0){
//부모 element를 꺼내서
int parentIdx = (int)Math.floor((index -1) / 2);
int parent = list.get(parentIdx);
//새로운 element와 비교한다.
if(element > parent){
//새로운 값이 부모보다 크다면 서로 바꾼다.
list.remove(parentIdx);
list.add(parentIdx, element);
list.remove(index);
list.add(index, parent);
index = parentIdx;
}else{
//새로운 값이 부모보다 크지 않다면 bubble up을 멈춘다.
break;
}
}
return list;
}
public ArrayList<Integer> extractMax(ArrayList<Integer> list){
int max = list.get(0);
//추출한 최대값 출력
System.out.prinln(max);
list.remove(0);
//만약 하나밖에 없었다면... OutofIndex방지
if(list.size() > 0){
//list의 맨 끝 값 가져오기
int end = list.get(list.size()-1);
list.remove(list.size()-1);
//끝값을 가장 첫번째에 넣기
list.add(0, end);
//0번 index부터 비교하며 내려가기 + 정렬
list = sinkDown(list);
}
return list;
}
public ArrayList<Integer> sinkDown(ArrayList<Integer> list){
int index = 0;
int length = list.size() - 1;
int element = list.get(0);
while(true){
int leftChildIdx = 2 * index + 1;
int rightChildIdx = 2 * index + 2;
int leftChild, rightChild;
int swap = null;
//왼쪽 오른쪽 자식중에 더 큰 애를 골라서 swap할 수 있게 해당 index를 찾는다.
if(leftChildIdx < length){
leftChild = list.get(leftChildIdx);
if(leftChild > element){
swap = leftChildIdx;
}
}
if(rightChildIdx < length){
rightChild = list.get(rightChildIdx);
if((swap == null && rightChild > element) || (swap != null && rightChild > leftChild)){
swap = rightChildIdx;
}
}
//swap index가 없다면 이대로 끝
if(swap == null) break;
//index의 값보다 큰 좌우 자식중 큰 값을 index의 값과 바꾸고
list.replace(index, list.get(swap));
list.replace(swap, element);
//mother index를 바꾸고 처리를 계속이어나간다.
index = swap;
}
return list;
}
}
ExtractMax (Removing)
root에 있는 가장 큰 수를 지우고 Array index 마지막에 해당하는 value와 swap한다.
그 후 sinking down이라고 하는 bubble 정렬 과정을 통해 다시 sorting한다.
Priority Queue
우선순위가 높은 것이 먼저 out되는 Queue를 말한다. Heap의 핵심이다!!!!!(insert와 Extractmax를 합치면 완성)
Array로 구현한다면…?
{3,1,2,5,4}가 있다면 2번째에 가장 우선되는 작업이 있다는 것을 반드시
모든 array를 훑어본 후에야 알 수 있기 때문에 작업을 할때마다 그것을 해야하는건 너무 비효율적이다.
O(n)의 시간복잡도를 가진다.
Heap!
Insert를 하면 알아서 정렬이 되고, ExtractMax를 통해 root에 있는 최우선순위의 value가 빠져나가고 heap은 다시 재배치 된다.
O(log n)의 복잡도를 가진다.
Big O Notation
| methods | Big O notation |
|---|---|
| insert | O(log n) |
| dequeue | O(log n) |
| Search | O(n) |