Object Oriented Programming in JS
Class가 아닌 Prototype 기반의 JS 객체지향 프로그래밍의 이론과 방법 모음집.
What is OOP?
-
Object-oriented programming(OOP)is a programming paradigm based on the concept of objects(= Style of the code, “how” we write and organize code)
-
Use objects to model(describe) real-world(E.g. user or todo list item) or abstract features(E.g. HTML component or data structure)
-
Object may contain data (properties) and code(methods). By using objects, we pack data and the corresponding behavior into one block
-
Objects are building blocks of applications, and interact with one another
-
Interactions happen through a public interface(aka. API): method that the code outside of the object can access and use to communicate with the object.
-
OOP was developed with the goal of organizing code, to make it more flexible and easier to maintain(avoid “spagghetti code”)
OOP in Javascript
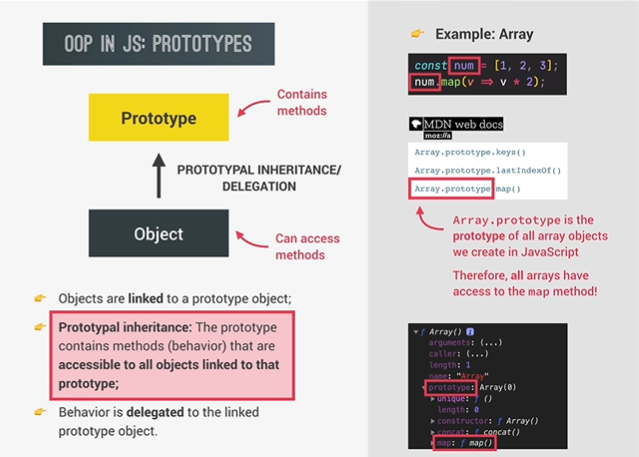
모든 Object들은 자신들의 모체인 Prototype object를 바라보고 있으며 그것을 inheritance하고 있다. 따라서 prototype이 가진 method들도 object에서 모두 사용이 가능하다.(e.g. Array의 method를 모든 Array객체에서 사용 가능하다.)
반면, 전통적인 OOP에선 class에 쓰여진 모든 property와 method들이 instance에 복사되어 하나의 객체가 된다.
Object들 만드는 3가지 방법
- Constructor functions
JS가 만들어질때 부터 있던 객체 생성 방법
- ES6 Classes
전통적인 class를 통한 객체 생성 방법이지만 실제 객체 생성 방법은 전통 class방식이 아닌 JS의 방식을 따른다.
- Object.create()
object를 prototype object로 잇기 위한 가장 직관적인 방법
Constructor functions
new 키워드를 사용해 instance를 만들어내는 것으로, JS가 생겨날 때부터 있었던 객체 생성 방법이다.
객체 생성 과정
- New {} is created
새로운 빈 객체 생성
- function is called, this = {}
객체의 모태가 되는 function을 부른다. constructor funtion이라고도 한다. constructor function은 작성된 function을 모태로 만들어지며 function과 연결되있는 prototype object에 들어있다.
- {} linked to prototype
새로 만들어진 instance는 자신의 모체인 prototype을 바라본다. 해당 링크는 __proto__라는 property 이름으로 등록된다.
- function automatically return {}
constructor function이 알아서 새로 만들어진 instance를 return해 변수에 연결시킨다.
prototype Extend 주의 할 점
원래 주어지는 prototype의 확장을 하면 안되는 이유
- JS의 다음버전이 나올 때, 내가 추가한 method의 이름과 같다면 덮어 씌워져서 치명적인 오류가 발생할 수 있다.
- 팀으로 개발할 시에 같은 기능을 서로 다른 이름으로 추가 하는 등의 엇갈림으로 큰 문제가 될 수 있다.
Classes in ES6
Class 문법을 통해 만들어지는 JS의 Object를 살펴본다
class PersonCl{
//function 그 자체가 constructor가 되었던 전통적인 JS 방식과는 달리
//Class에선 반드시 constructor function을 지정해줘야 한다.
//New로 Object를 만들시에는 이 constructor function이 발동되어 Object를 만든다.
constructor(firstName, birthYear){
this.firstName = firstName;
this.birthYear = birthYear;
}
//중요!! constructor 바깥, class 안에 쓰는 method들은 모두 prototype object에 귀속된다!!
//method 추가 방법
calcAge(){
console.log(2020 - this.birthYear);
}
}
const jessica = new PersonCl('Jessica', 1995);
console.log(jessica.__proto__ === PersonCl.prototype); //true
class 사용시 주의점
- classes are NOT hoisted
즉, class가 선언이 되어있어도 function처럼 바로 사용하지 못한다.
- Classes are first-class citizen
class문법이긴해도 object생성 방법은 JS의 원리를 그대로 따르기 때문
- Classes are executed in strict mode
???????????
Setter and Getter
이 특별한 property를 assesseor property라고 하며 (그 외는 data property라고 한다.) 밖에서 보기엔 그냥 일반 property와 같다.
주의사항
- property name과 setter의 이름이 같다면 property를 setting할 경우 setter를 발동, setter안에서 같은 property name이 있으니 이것이 또 setter 발동… 무한 루프에 빠지게 된다.
class Person {
constructor(fullName){
//여기서 바로 fullName이라는 이름의 setter 자동으로 발동
this.fullName = fullName;
}
set fullName(name){
//fullName이라는 이름의 setter 자동으로 발동....
//무한반복! = error
this.fullName = fullName;
//따라서!! convention으로 property name은 '_'을 앞에 붙여준다.
this._fullName = fullName;
}
}
static
constructor function에만 붙어있고 prototype object에는 귀속되지 않아 instance들에 상속되지 않는 특별한 method이다.
//Array가 아닌 열거형을 Array로 만들어 주는 method
Array.from(document.querySelectorAll('h1'));
[1,2,3].from(); //error
Number.parseFloat(12);
123.parseFloat(); //error
//추가 방법
//일반 방법
const Person = function(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
var jonas = new Person('Jonas', 23);
Person.hey = function(){
console.log('Hey!');
console.log(this); //Person의 constructor function
}
Person.hey();
jonas.hey(); //error
//class의 경우
class PersonCl{
constructor(name, age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//aka. instance method
//.propertype property에 추가 되어 모든 instance가 이 method를 사용할 수 있으므로
calcAge(){
console.log(2020 - this.age)
}
static hey(){
console.log('Hey!');
console.log(this); //Person의 constructor function
}
}
PersonCl.hey();
Object.create
instance를 만드는데는 많이 쓰이지 않지만 각 custom class혹은 function끼리의 inheritance에 중요한 역할을 한다.
//Object.create() 함수의 내부 로직, 프로토타입 상속의 원리를 보여준다
function create_object(o){
function F() {}
F.prototype = o;
return new F();
}
New 키워드와 다른점
-
new - Object를 만들때 자동으로 constructor function의 prototype object를 link한다
-
object.create() - 내가 원하는 object를 prototype 로서 지정해 줄 수 있다, constructor function이 필요없다.
How do we actually design classes?
좋은 class를 설계하기 위해선 4가지의 법칙이 있다.
Abstraction
Ignoring or hiding details that don’t matter, allowing us to get an overview perspective of the thing we’re implementing, instead of messing with details that don’t really matter to our implementation.
ex) 우리가 이벤트 리스너를 지정할때, eventListner를 사용하지만 그 안의 logic까지 신경쓰지 않는다.
Encapsulation
Keeping properties and methods private inside the class, so they are not accessible from outside the class. Some methods can be exposed as a public interface(APIs)
프로그램이 커질 수록 object안의 data를 직접 건드리는 것은 버그를 발생 시키기 쉬우므로 하나의 class에 필요한 것만 드러내는 것이 중요하다.
Inheritance
Making all properties and methods of a certain class available to a child class, forming a hierachical realationship between classes. This allows us to reuse common logic and to model real-world relationships.
Polymorphism
A one child class overwrite a method it inherited from a parent class