Trees
Parent Child 관계를 가진 데이터 구조로 Root Directory로 부터 내려간다.
Rules
- 모든 Parent node는 최대 2개의 child를 가질 수 있다.
- Parent node보다 좌측의 node는 Parent보다 항상 작다.
- Parent node보다 우측의 node는 Parent보다 항상 크다.
대표적인 예가 바로 윈도우의 파일 구조이다.
Tree Terminology
- Root : Tree의 가장 Top
- Child : 다른 node와 직접적으로 연결 된 node, 부모의 하위 개념이 된다.
- Parent : Child의 부모
- Siblings : 같은 부모를 가진 다른 Child node
- Leaf : Children이 없는 node
- Edge : 어떤 node와 다른 node의 연결
Kinds of Trees
- Trees
- Binary Trees
- Binary Search Trees
big O notation
| methods | big O notation |
|---|---|
| insert | O(log N) |
| search | O(log N) |
| delete | O(log N) |
pros & cons
| pros | cons |
|---|---|
| Better than O(n) | No O(1) Operation |
| Ordered | |
| Flexible size |
Examples
- HTML DOM(Document Object Model)
- Network Routing
- abstract syntax tree
- AI(경우의 수 판단, 분석 시)
- OS’s Folder System
Unbalanced Binary Search Tree(!!!)
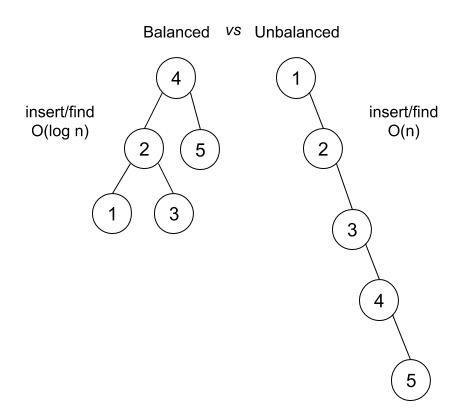
제대로 정렬되있지 않은 tree는 이런식으로 길게 늘어져 linked list와 같은 형태를 가지게 된다.
해결하는 방법은 길쭉한 line의 가운데 값을 root로 삼아 양 옆으로 데이터를 분산 하는 방법이다.
reference(AVL과 Red,Black의 작동원리를 애니메이션)
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/AVLtree.html
https://www.cs.usfca.edu/~galles/visualization/RedBlack.html
Red/Black tree, AVL tree
이 두가지 tree Data structure는 너무 치우쳐 있다면 알아서 balance를 잡을 수 있도록 해주는 tree로서 tree가 길게 늘어지지 않게 한다.
3개가 한줄로 이루어져 있을 때, 그 가운데 값을 root로 두고 나머지를 양 옆으로 분산하여 tree구조의 balace를 맞춘다.